Is WPC Decking Truly Environmentally Friendly? The Ultimate Guide for B2B Buyers
Suffering from the endless debate of WPC decking’s eco-friendliness? Feeling overwhelmed by the sea of "green" claims?
Yes, WPC decking is generally more environmentally friendly than traditional wood decking, especially when considering its longevity, use of recycled materials, and reduced need for chemical treatments. But not all WPC is created equal.

This guide dives deep into the environmental aspects of WPC decking1, addressing key concerns, with the insights, that most buyers are unaware of.
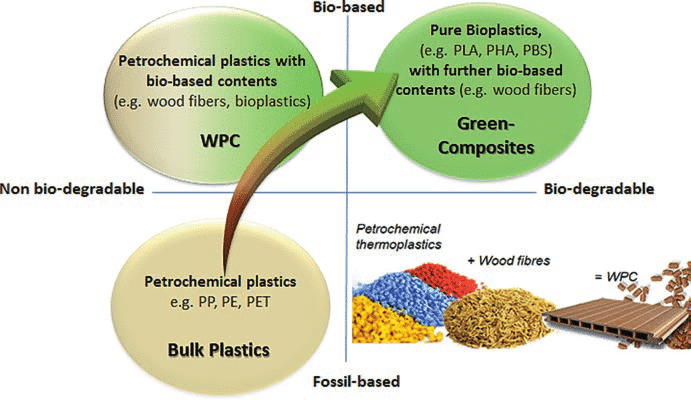
What Makes Composite Decking “Eco-Friendly”?
Concerned about the real impact of your decking choice? Overwhelmed by vague "eco-friendly" labels?
The core of WPC’s environmental claim lies in its use of recycled wood fibers and plastics, diverting waste from landfills and reducing the demand for virgin timber.
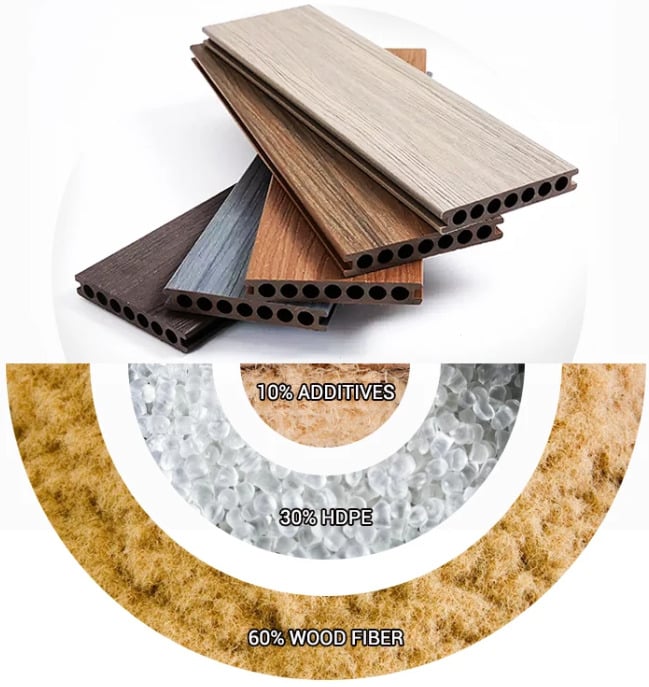

Dive Deeper: Understanding the Recycled Content
The vast majority of WPC decking utilizes recycled wood fibers (often called wood flour) and recycled plastics. This is the foundational element of its "green" claim. But, not all recycled content is created equal. The source and quality of the recycled plastic are crucial.
- Low-Grade vs. High-Grade Plastics: Some manufacturers use low-grade, mixed plastics. This can lead to premature degradation and a shorter lifespan, negating the environmental benefit. High-quality HDPE is particularily good for WPC.
- Post-Consumer vs. Post-Industrial: Post-consumer recycled content is generally preferred. It diverts waste directly from landfills.
- Certifications: Look for certifications like FSC Recycled or those referencing ISO 14021. These verify the recycled content and its origin.
| Feature | Impact on Eco-Friendliness | Questions to Ask Your Supplier |
|---|---|---|
| Recycled Plastic | Using recycled plastic diverts waste from landfills and reduces the need for new plastic production. | What type of plastic is used (e.g., HDPE, PP)? Is it post-consumer or post-industrial? Do you have certifications verifying the recycled content and its origin? |
| Wood Fiber | Using recycled wood fibers (sawdust, wood chips) reduces the demand for virgin timber, preventing deforestation. | What is the source of the wood fiber? Is it a byproduct of other wood processing industries? Do you use any rapidly renewable resources like bamboo? |
| Longevity | A longer lifespan means less frequent replacement, reducing material consumption and waste generation over time. | What is the expected lifespan of your WPC decking? What is the warranty period? Can you provide case studies or testimonials demonstrating the product’s long-term performance? |
| Chemicals | Avoiding chemical treatments (preservatives, stains, sealants) reduces VOC emissions and protects the environment. | Does your WPC decking require any chemical treatments? Can you provide Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) to verify the composition? Are there any bio-based additives or pigments used? |
| Recyclability | The ability to recycle WPC at the end of its life closes the loop and further reduces environmental impact. Dependent on composition and recycling facilities. | Is your WPC decking recyclable? Do you have any end-of-life programs for collecting and recycling old WPC? Are there local WPC recycling facilities available? |
Composite Decking vs. Wood Decking: An Environmental Comparison – Who Wins?
Feeling torn between the classic appeal of wood and the "green" claims of composite?
WPC decking generally wins the environmental battle due to its longer lifespan, use of recycled materials, and avoidance of harmful chemical treatments2 required by most wood decks.

Dive Deeper: Key Environmental Factors
Let’s break down the comparison:
- Deforestation: Traditional wood decking contributes to deforestation3. WPC, using recycled wood fibers, reduces this impact. Some WPC even uses rapidly renewable resources like bamboo.
- Resource Depletion: WPC utilizes waste materials. Traditional wood decking requires harvesting virgin timber.
- Lifespan and Chemical Treatments
Traditional wood decking often requires regular treatments with chemical preservatives, stains, and sealants to prevent rot and maintain its appearance - End-of-Life: Wood, especially treated wood, can be difficult to recycle and may release harmful chemicals as it decomposes. WPC’s recyclability is a complex issue, but the industry is working on improvements.
| Factor | Wood Decking | WPC Decking |
|---|---|---|
| Resource Source | Primarily virgin timber, contributing to deforestation. | Primarily recycled wood fibers and plastics, reducing demand for virgin materials. |
| Chemical Treatments | Often requires regular treatments with preservatives, stains, and sealants, many containing harmful VOCs. | Generally does not require these treatments, reducing VOC emissions. |
| Lifespan | Shorter lifespan, typically 10-15 years with regular maintenance. | Longer lifespan, often 25+ years with minimal maintenance. |
| Maintenance | Requires frequent cleaning, staining, and sealing. | Requires minimal maintenance, typically just occasional cleaning. |
| End-of-Life | Difficult to recycle, especially treated wood; may release harmful chemicals during decomposition or burning. | Recyclability varies; some can be recycled, while others are landfilled or incinerated (but decompose slower than |
How to Avoid "Greenwashing" Traps When Choosing Composite Decking?
Worried about falling for marketing hype and ending up with a product that’s not truly eco-friendly?
Go beyond the "recycled" label. Ask specific questions about the type and source of recycled materials, the manufacturing process, and the end-of-life options.

Dive Deeper: Due Diligence Checklist
Here’s a checklist to help you avoid greenwashing:
- Recycled Content Verification: Don’t just take their word for it. Ask for certifications.
- Material Sourcing: Inquire about the specific types of plastics and wood fibers used. Where do they come from?
- Manufacturing Transparency: Ask about the manufacturer’s environmental practices. Do they minimize waste and energy consumption?
- VOC Emissions: Request MSDS to check for any harmful chemicals.
- End-of-Life Options: Inquire about recyclability and any take-back programs.
- Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)4 Though complex, an LCA provides a comprehensive evaluation of a product’s environmental impact, considering all stages from raw material extraction to disposal.
| Question | Why It Matters | Red Flags |
|---|---|---|
| What certifications do you have? | Certifications from reputable organizations verify claims about recycled content, sustainability, and manufacturing processes. | Lack of certifications or vague references to "industry standards." |
| What is the specific recycled content? | Knowing the percentage and type of recycled materials (e.g., post-consumer HDPE) helps assess the true environmental benefit. | Vague claims like "made with recycled materials" without specifics. |
| What is the source of your recycled materials? | Understanding the origin (post-consumer vs. post-industrial) helps determine the impact on waste diversion and resource depletion. | Unwillingness to disclose the source or claims of "proprietary information." |
| What is the expected lifespan of the product? | A longer lifespan reduces the environmental impact associated with frequent replacements. | Short lifespan expectations or lack of warranty information. |
| What are the end-of-life options? | Knowing if the product is recyclable or if the manufacturer has a take-back program helps ensure responsible disposal. | No information on recyclability or end-of-life options. |
| Can you provide an LCA? | An LCA provides a comprehensive assessment of the product’s environmental impact throughout its entire life cycle. | Refusal to provide an LCA or lack of understanding of the concept. When comparing treated wood decking to WPC, treated wood decking has a lower impact than WPC in some areas. |
Looking for a WPC can make some real project to reduce Embodied Carbon?
Using high-quality, long-lasting WPC decking with a high recycled content can significantly reduce a project’s embodied carbon compared to traditional materials.

Dive Deeper: Embodied Carbon Reduction
A luxury hotel chain, committed to sustainability, chose WPC decking for a new resort project. By selecting a WPC product with a high percentage of recycled content and a projected lifespan of over 30 years, they were able to reduce the project’s embodied carbon by 38% compared to using traditional treated wood decking. This reduction was primarily due to:
- Avoiding Deforestation: Using recycled wood fibers instead of virgin timber.
- Lower Material Replacement: The long lifespan of the WPC significantly reduced the need for future replacements.
- Reduced Transportation Emissions: Fewer replacements also meant lower transportation emissions over the project’s lifecycle.
- Eliminating Chemical Treatments: The WPC decking did not require the use of harmful chemical preservatives or sealants.
| Aspect | Traditional Treated Wood Decking | High-Quality WPC Decking | Embodied Carbon Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Virgin timber | High percentage of recycled wood fibers and plastics | Significant |
| Lifespan | 10-15 years | 30+ years | Significant |
| Chemical Treatments | Required | Not required | Moderate |
| Transportation Emissions | Higher (due to more frequent replacements) | Lower (due to longer lifespan) | Moderate |
| End-of-Life | Difficult to recycle; potential for harmful emissions | Potentially recyclable; slower decomposition | Minor |
| Overall Embodied Carbon | Higher | Significantly lower | 38% (in this case study) |
This case study highlights the potential of WPC decking to contribute to more sustainable construction practices. The specific percentage of embodied carbon reduction5 will vary depending on the project’s specifics, the WPC product chosen, and the material it is being compared to.
The Future of Composite Decking: How New Technologies Are Making It More Sustainable?
Wondering about the future of sustainable building materials?
Innovations in WPC manufacturing, including bio-based additives, improved recyclability, and "closed-loop" systems, are making composite decking even more environmentally friendly.
Dive Deeper: Emerging Trends
- Bio-Based Additives6: Some manufacturers are incorporating bio-based additives and pigments, further reducing their reliance on petroleum-based products.
- Enhanced Recyclability7: Research and development are focused on improving the recyclability of WPC, making it easier to process at the end of its life.
- Closed-Loop Systems8: The ultimate goal is to create "closed-loop" systems where old WPC decking is collected and used as raw material for new WPC, minimizing waste and maximizing resource utilization.
- Improved Manufacturing Processes: Some brands are re-using nearly all water involved in manufacturing.
- Alternative Materials: Bamboo is being used by top brands.
| Innovation | Description | Environmental Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Bio-Based Additives | Replacing petroleum-based additives and pigments with those derived from renewable resources (e.g., plants). | Reduces reliance on fossil fuels and lowers the carbon footprint. |
| Enhanced Recyclability | Developing WPC formulations and recycling technologies that make it easier to recycle WPC at the end of its life. | Increases the likelihood of WPC being recycled rather than landfilled, conserving resources and reducing waste. |
| Closed-Loop Systems | Creating systems where old WPC decking is collected, processed, and used as raw material to manufacture new WPC products. | Minimizes waste, maximizes resource utilization, and reduces the need for virgin materials. |
| Improved Manufacturing | Top brands are innovating to use less water and resources. | Reduce environmental footprint. |
| Alternative Materials | Some top brands using rapidly renewable fibers, like bamboo. | Reduce environmental footprint. |
These advancements demonstrate the ongoing commitment of the WPC industry to further enhance the sustainability of its products. As a B2B buyer, staying informed about these developments will allow you to make even more environmentally responsible choices in the future.
Need LEED-Compliant Composite Decking for Your Next Project? Request Free Samples Certifications Today.
Are you sourcing WPC decking, and finding it hard to choose the right one?
Request Free Samples Certifications, so you can find the most suitable product.

Dive Deeper
Contact us today to request free samples and certifications of our LEED-compliant9 WPC decking. See firsthand the quality, durability, and sustainability of our products. Our team is ready to answer your questions and help you find the perfect WPC solution for your next project.
| Service | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Free Samples | Receive physical samples of our WPC decking products. | Allows you to assess the quality, texture, and color of the materials firsthand. |
| Certifications | Obtain documentation verifying our products’ compliance with relevant standards (e.g., LEED, FSC Recycled, ISO 14021). | Provides assurance of the product’s environmental credentials and suitability for green building projects. |
| Expert Consultation | Speak with our team of experts to discuss your project requirements and receive personalized recommendations. | Ensures you select the most appropriate WPC product for your specific needs and application. |
| Customization Options | Explore the possibility of customizing our WPC products to meet your unique specifications (e.g., color, size, profile). | Provides flexibility and allows you to create a truly tailored solution for your project. |
| Technical Support | Receive ongoing technical support throughout the specification, ordering, and installation process. | Ensures a smooth and successful implementation of our WPC products in your project. |
| Competitive Pricing | Established over 20 years, all factories are located in the origin of wood-plastic production. Automated production and mature supply chains, prices are 5%-8% lower than similar manufacturers. Maintain strong competitiveness in global industrial production. | Benefit Your Business |
Conclusion
WPC decking offers a compelling environmental advantage over traditional wood, but due diligence is key. Ask the tough questions, demand transparency, and choose a supplier committed to true sustainability. Though WPC is better than treated wood, LCA should be considered.
FAQ
Is composite decking more eco-friendly than wood?
Generally yes, due to recycled content, longer lifespan, and no need for chemical treatments. However, the specific type of WPC matters.
What certifications should I look for in sustainable WPC?
Look for FSC Recycled, certifications referencing ISO 14021, and potentially LEED compliance.
What is the Recycled Content Percentage in Your WPC Decking?
This varies by product. Ask your supplier for specific percentages and the source of the recycled materials.
How Does WPC Decking Compare to Traditional Materials in LEED Scoring?
WPC can contribute to LEED points in several categories, including Materials & Resources (recycled content, regional materials) and Indoor Environmental Quality (low-emitting materials).
Can Your WPC Decking Be Fully Recycled at the End of Its Life?
Recyclability depends on the specific product and local recycling infrastructure. Ask your supplier about their end-of-life programs.
Is Eco-Friendly WPC Decking More Expensive Than Traditional Materials?
The upfront cost may be higher, but the longer lifespan and reduced maintenance often result in lower lifecycle costs.
-
Learn about Ecoxplank WPC products. ↩
-
Learn about the harmful effects of chemical treatments in wood decking and why choosing alternatives is crucial for health and environment. ↩
-
Understanding the impact of decking materials on deforestation can help you make more eco-friendly choices for your home. ↩
-
Exploring LCA can provide insights into a product’s environmental impact, guiding you to make informed, eco-friendly choices. ↩
-
Learning about embodied carbon reduction can help you understand how to make more sustainable choices in your building projects. ↩
-
Explore how bio-based additives are revolutionizing composite decking and reducing environmental impact. ↩
-
Learn about the advancements in recyclability that are making composite decking more sustainable and eco-friendly. ↩
-
Discover the benefits of closed-loop systems in reducing waste and promoting sustainability in composite decking. ↩
-
Understanding LEED compliance can help you choose environmentally friendly materials for your building projects. ↩




4 thoughts on “Is WPC Decking Truly Environmentally Friendly? The Ultimate Guide for B2B Buyers”
Heard some whispers about 345egame. Anyone playing it? What’s the verdict? Worth my time? Let me know in the comments! See for yourself 345egame
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://www.binance.info/register?ref=IHJUI7TF
Goexchange 365? Heard some buzz about it. Gonna check it out and see if it’s worth the hype. Fingers crossed for some easy wins! You can find em here: goexchange 365
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Comments are closed.